Financial Risk Manager Introduction
Contents
The Financial Risk Manager (FRM) Certification is the true standard for educational excellence in risk management and a gateway to achieving new career heights in the risk profession.
Key Concepts
Interest Rates
Required Rate of Return
- Required rate of return / 要求回报率 / yield
- Influenced by the
supply and demand of fundsin the market. - Represents the return that investors and savers need to convince them to willingly lend their money.
- Typically associated with a specific investment.
- Example: If I deposit my money in a bank, what would the interest rate be?
- In this case:
- Interest rate = Required Rate of Return = Real Risk-free Return (真实无风险收益率) + Inflation Rate (通货膨胀收益率)
- Breaking down the required rate of return:
- Nominal risk-free rate = real risk-free rate + expected inflation rate.
- Required interest rate on a security = nominal risk-free rate + default risk premium + liquidity risk premium + maturity risk premium.
Discount Rate
- Discount rate / 折现率
- This is the interest rate used to
discount future payments. - It is often used interchangeably with the term “interest rate”.
- Depending on the situation, “interest rate” can have different names:
- Example 1: I deposit $100 in a bank for one year and receive a 10% interest rate. After one year, I have 110.
- In this scenario, the 10% interest rate is referred to as the 10% Required Rate of Return.
- Example 2: I want to have $10 after one year. If the interest rate is 10%, how much should I deposit in the bank? Using the formula (x+10)/(1+10%) = x, we find x = 100.
- In this scenario, the 10% interest rate is referred to as the 10% Discount Rate.
- Example 1: I deposit $100 in a bank for one year and receive a 10% interest rate. After one year, I have 110.
Opportunity Cost
- Opportunity cost / 机会成本
- This can be seen as a type of interest rate. It represents the value that investors give up when they choose a particular course of action.
Basic Calculation
Future Value (FV)
- Amount to which investment grows after one or more compounding periods
Present Value (PV)
Current value of some future cash flow
If interests are compounded m times per year, and
invest 1 year:If interests are compounded m times per year, and
invest n years:Where:
mis the compounding frequency;ris the nominal / quoted annual interest rate
Simple Interest
Simple Interest / 单利
Interest is compounded annually at 10% per annum
sequenceDiagram Note over Start Deposit: PV = 100$ Start Deposit->>First Year End: 10% Note over First Year End: 100+100*10% First Year End->>Second Year End: 10% Note over Second Year End: FV = 100+100*10%*2sequenceDiagram Note over Start Deposit: PV = 100$ Start Deposit->>First Year End: 10% Note over First Year End: 100+100*10% First Year End->>Second Year End: 10% Note over Second Year End: FV = 100+100*10%*2
Compound Interest
Compound Interest / 利滚利
Interest is compounded annually at 10% per annum
sequenceDiagram Note over Start Deposit: PV = 100$ Start Deposit->>First Year End: 10% Note over First Year End: 100*(1+10%) First Year End->>Second Year End: 10% Note over Second Year End: FV = 100*(1+10%)^2sequenceDiagram Note over Start Deposit: PV = 100$ Start Deposit->>First Year End: 10% Note over First Year End: 100*(1+10%) First Year End->>Second Year End: 10% Note over Second Year End: FV = 100*(1+10%)^2
Continuously Compounding:
- Interest is compounded
mtimes per year at an annual rate ofr%, then afternyears
Annuity
- Annuity / 年金
- Annuity is a stream of
equal cash flowsthat occurs atequal intervalsover a given period - Classify:
- Annuity due - 先付年金(年初支付)
- Ordinary annuity - 后付年金(年末支付)
Framework of FRM Program
Outline
PART Ⅰ
- Foundations of Risk Management 风险管理基础(20%)
- 基础知识,学完其他三门基本掌握该部分知识
- Quantitative Analysis 数量分析(20%)
- 金融:在不确定的情况下,资产的跨期配置
- 概率论和统计学
- Financial Markets and Products 金融市场与金融产品(30%)⭐
- Part Ⅰ 3/4 是二级
市场分险的基础 - Part Ⅰ 3/4 最好放在一起学习
- Part Ⅰ 3/4 是二级
- Valuation and Risk Models 估值与风险建模(30%)⭐
PART Ⅱ
- Market Risk Measurement and Management 市场分险测量与管理(25%)
- Credit Risk Measurement and Management 信用分险测量与管理(25%)
- Operational and Integrated Risk Management 操作及综合风险管理(25%)
- Risk Management and Investment Management 投资风险管理(15%)
- Current Issues in Financial Markets 金融市场前沿话题(10%)
PART Ⅰ
Foundations of Risk Management
- Risk Management (Best practice)⭐
- Risk management and Corporate Governance Perspective
- Implementing Risk Appetite Frameworks
- Principles for Effective Data Aggregation and Risk Reporting
- Risk Management Failures
- Capital Asset Pricing Model (Theory)⭐⭐⭐
- The Standard Capital Asset Pricing Model
- Arbitrage Pricing Theory and Multifactor Models of Risk and Return
- Applying the CAPM to Performance Measurement
- Information Risk and Data Quality Management
- Financial Disasters⭐⭐
- The Credit Crisis of 2007
- GARP Code of Conduct
Risk
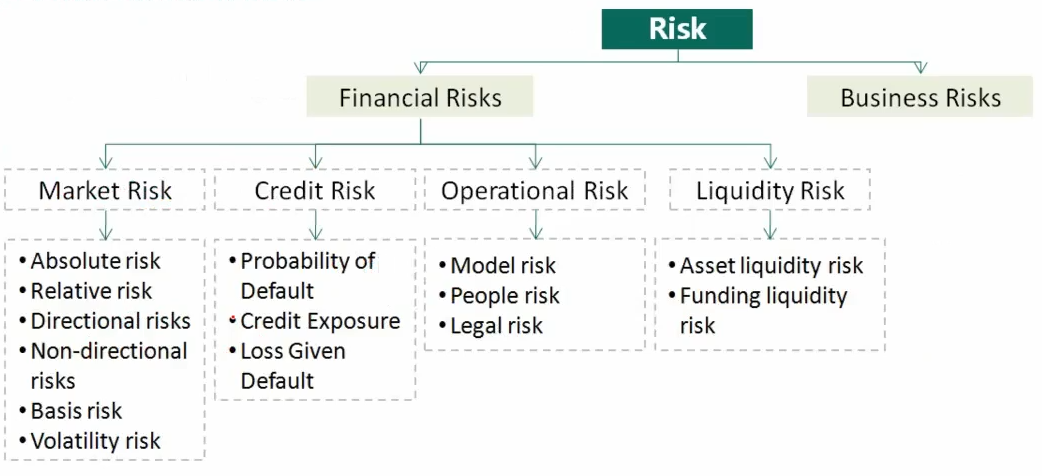
- Definition of Risk
- Risk is defined as the unexpected variability of asset prices and/or earnings. It is a mix of danger and opportunity
- Sources of Risk
Business riskis the risk that a firm is subjected to during daily operations and includes the risks that result from business decisions and the business environmentFinancial risksare the results of a firm’s financial market activities
Quantitative Analysis
- Probability
- Basic Statistics
- Distributions
- Hypothesis Tests and Confidence Intervals
- Linear Regression
- Linear Regression with One Regressor
- Linear Regression with Multiple Regressors
- Simulation Modeling⭐
- Estimating Volatilities and Correlations⭐
- Correlation and Copulas
Financial Markets and Products
- Derivative Contract
- Structure and mechanics of OTC and exchange markets
- Structure, mechanics, and valuation of Derivative Contracts
- Forwards, Futures and Swaps
- Options
- Hedging wit derivatives
- Financial Product (Fixed Income)
- Interest rates and measures of interest rate sensitivity
- Foreign exchange risk
- Corporate bonds
- Mortgage-backed securities
- Rating agencies
Valuation and Risk Models
- Valuation
- Option valuation
- Fixed income valuation
- Risk Models
- Value-at-Risk (VaR)
- Expected shortfall (ES)
- Stress testing and scenario analysis
- Risk Management
- Hedging
- Country and sovereign risk models and management
- External and internal credit ratings
- Expected and unexpected losses
- Operational risk