Unveiling the Top Frequency Leetcode and Crafting Effective Solutions
Contents
F1 - 🟨146. LRU缓存机制
关键字
| 关键字 | 对应信息 |
|---|---|
| 键值对 | |
| put 和 get 的时间复杂度为O(1) | 哈希表,而且可以通过 O(1) 时间通过键找到值 |
| 有出入顺序 | 首先想到 栈,队列 和 链表。哈希表无固定顺序 |
补充
哈希链表 LinkedHashMap 直接满足要求
解题
哈希表可以满足 O(1) 查找;
链表有顺序之分,插入删除快,但是查找慢。
于是就有了哈希链表数据结构:
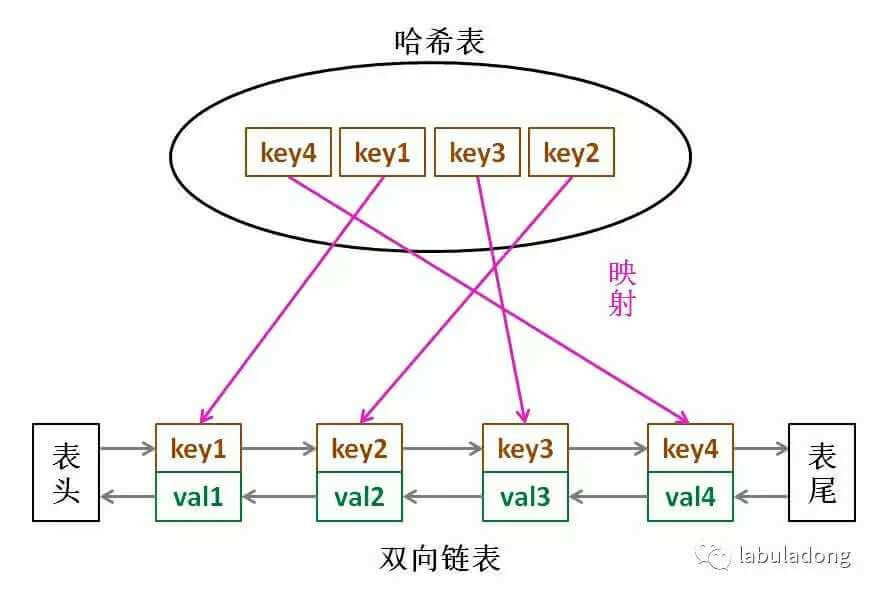
为什么使用双链表而不使用单链表?
删除操作也可能发生在链表的中间位置。如果使用单链表,删除节点时需要额外找到被删除节点的前驱节点,这会增加时间复杂度。
哈希表中已经存了
key,为什么链表中还要存key和val呢,只存val不就行了?
public class LRUCache {
class Node{
int key;
int val;
Node preNode;
Node nextNode;
Node(int key, int val){
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<Integer, Node>();
int size;
int capasity;
Node head, tail;
public LRUCache(int capasity){
this.capasity = capasity;
size = 0;
head = new Node(0, 0);
tial = new Node(0, 0);
head.nextNode = tail;
tail.preNode = head;
}
public int get(int key){
Node node = map.get(key);
if(node == null){
return -1;
}
move2first(node);
return node.val;
}
public void put(int key, int val){
Node node = map.get(key);
if(node != null){
node.val = val;
move2first(node);
} else {
Node newNode = new Node(key, val);
map.put(key,newNode);
addNode(newNode);
size++;
if(size > capasity){
Node deleted = deleteLastNode();
map.remove(deleted.key);
size--;
}
}
}
private void move2first(Node node){
deleteNode(node);
addNode(node);
}
private void deleteNode(Node node){
node.preNode.nextNode = node.nextNode;
node.nextNode.preNode = node.preNode;
}
private void addNode(Node node){
node.nextNode = head.nextNode;
head.nextNode.preNode = node;
head.nextNode = node;
node.preNode = head;
}
private Node deleteLastNode(){
Node res = tail.preNode;
deleteNode(res);
return res;
}
}F2 - 🟩206. 反转链表
解题
- 方法一:双指针/三指针迭代
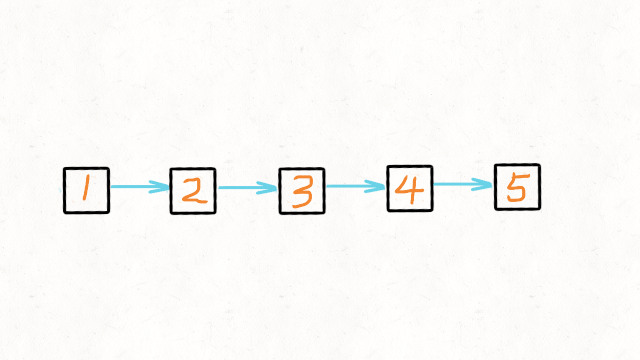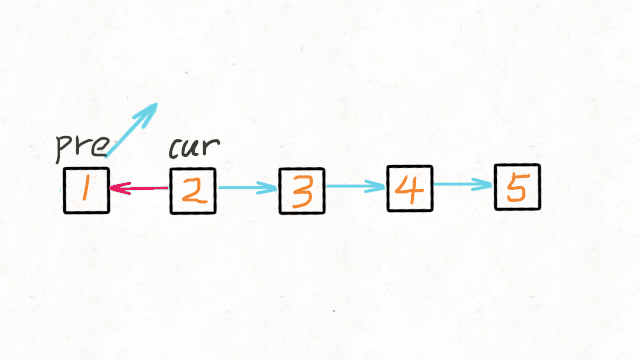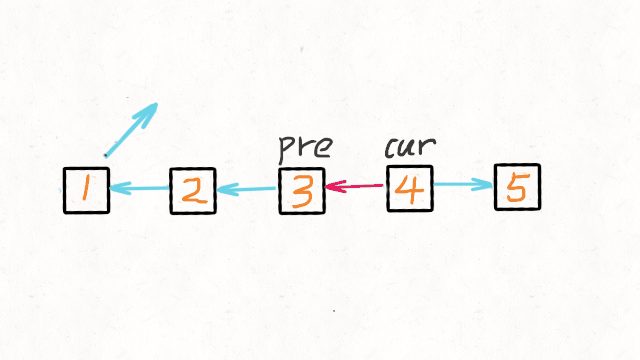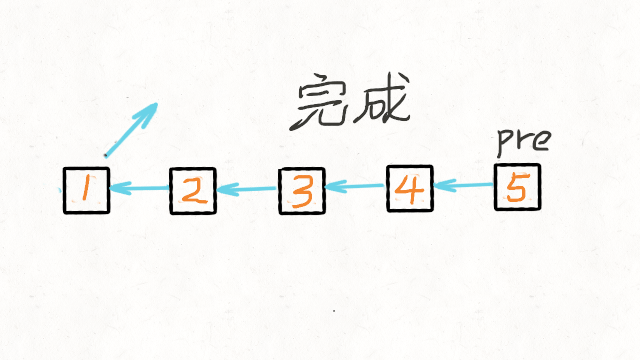
- 初始化节点
- pre 用来指向 cur 指针前一个节点。初始是 null,因为链表尾节点的下一节点是 null
- cur 指向当前节点。初始是 head
- tmp 用来指向 cur 节点的下一个节点。初始是 null
while(cur!=null), tmp 指向 cur 节点的下一个节点;修改 cur.next = pre; pre 指向 cur 相当于后移一位;cur 指向 tmp 相当于后移一位
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode tmp = null;
while(cur!=null) {
tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}- 方法二:递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null) {
return head;
}
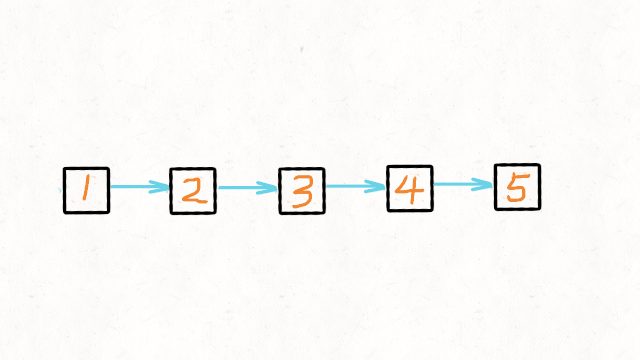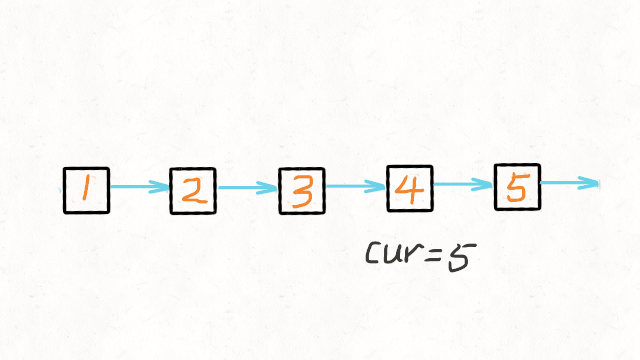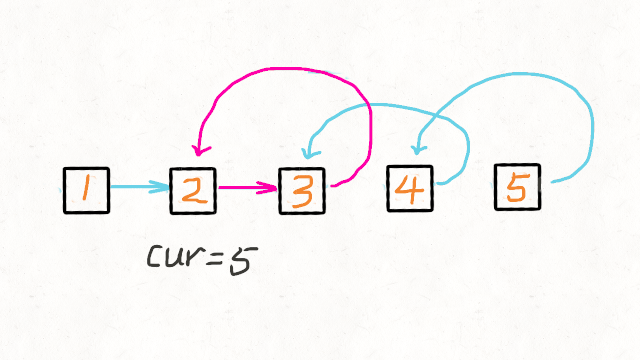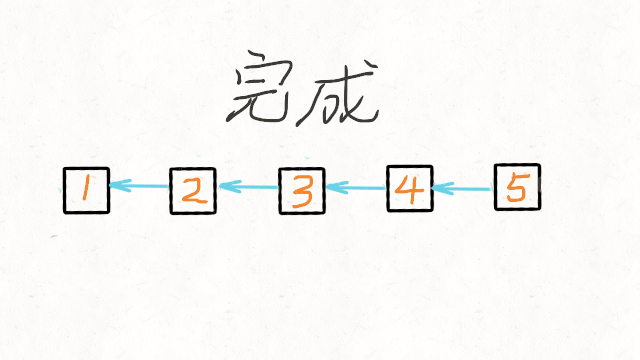
//这里的cur就是最后一个节点
ListNode cur = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return cur;
}
}- 方法三:利用外部空间
先申请一个动态扩容的数组或者容器,比如 ArrayList 这样的。 然后不断遍历链表,将链表中的元素添加到这个容器中。 再利用容器自身的 API,反转整个容器,这样就达到反转的效果了。 最后同时遍历容器和链表,将链表中的值改为容器中的值。
F3 - 🟨3. 无重复字符的最长子串
关键字
| 关键字 | 模式识别 |
|---|---|
重复字符(或者说出现一次以上) | 一旦涉及出现次数,需要用到 散列表 构造子串,散列表存下标 |
| 子串 | 涉及子串,考虑滑动窗口,滑动窗口就是队列 - 滑动窗口就是窗口扩张和窗口收缩 |
解题
class Solution{
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s){
int left = 0;
int max = 0;
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
for(int right = 0; right < s.length(); right++){
if(map,containsKey(s.charAt(right))){
//碰到了重复字符,使窗口左窗向移动到后面遇到的这个重复字符后面
left = Math.max(left, map.get(s.charAt(right)) + 1);
}
//在碰到重复字符之前,右窗口一直向右移动,并记录最大长度
map.put(s.charAt(right), right);
max = Math.max(max, right - left + 1);
}
return max;
}
}F4 - 🟥25. K 个一组翻转链表
解题
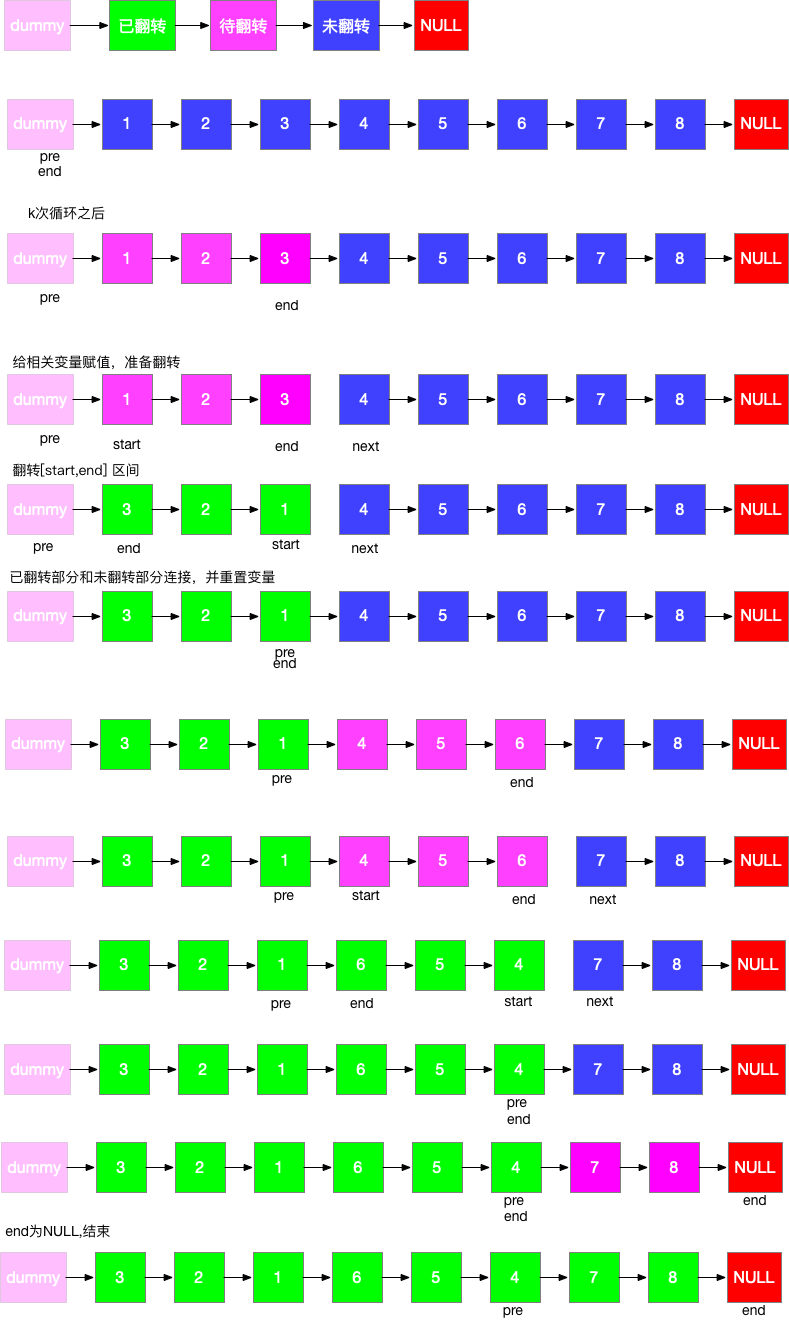

class Solution{
public Node reverseKGroup(Node head, int k){
Node dummy = new Node();
dummy.next = head;
Node pre = dummy;
Node end = dummy;
while(end.next != null){
for(int i = 0;i<k && end!=null; i++) end = end.next;
if(end==null) break;
Node start = pre.next;
Node nextStart = end.next;
end.next = null;
pre.next = reverse(start);
start.next = nextStart;
pre = start;
end = pre;
}
return dummy.next;
}
// 反转链表,固定方法
public Node reverse(Node head){
Node pre = null;
Node cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
Node next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}F5 - 🟨215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
关键字
| 关键字 | 模式识别 |
|---|---|
| 第 K 个 | 维护动态数据的最大最小值,可以考虑堆 建立容量为 k 的最小值堆 |
| 第 K 个 | 确定数量的情况下寻找第 K 大的数,可以利用快速选择算法 快速排序算法中的轴值计算 |
解题
PriorityQueue 可以看做是一个最大堆或最小堆
new PriorityQueue<Integer>()可以看做最小堆new PriorityQueue<Integer>(Comparator.reverseOrder())可以看做最大堆
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
// 使用 PriorityQueue 来作为最小堆,大小为 k
PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(k);
for (int num : nums) {
if (minHeap.size() < k) {
// 当优先队列不满时,直接插入
minHeap.add(num);
} else if (num > minHeap.peek()) {
// 如果当前元素大于堆顶(也就是最小)元素,替换堆顶元素
minHeap.poll();
minHeap.add(num);
}
}
return minHeap.peek();
}
}F6 - 🟨15. 三数之和
解题
排序 + 双指针 本题的难点在于如何去除重复解
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
// 1.排序数组
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 2.左指针为循环标志,中指针和右指针每次重置
for(int left = 0; left < nums.length - 2; left++){ // [length - 3] 是最后一次,刚好容下三个值
if(nums[left] > 0) break;
// 跳过重复
if(left > 0 && nums[left] == nums[left - 1]) continue;
int middle = left + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while(middle < right){
int sum = nums[left] + nums[middle] + nums[right];
if(sum > 0){ // 若和大于 0,说明 nums[R] 太大,R 左移
while(middle < right && nums[right] == nums[--right]); // 并跳过重复
}else if(sum < 0){ // 若和小于 0,说明 nums[L] 太小,L 右移
while(middle < right && nums[middle] == nums[++middle]); // 并跳过重复
}else{ // 若和等于 0, 加入结果
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(nums[left],nums[middle],nums[right])));
// 说不定还有满足的结果, R 左移, L 右移
while(middle < right && nums[right] == nums[--right]); // 并跳过重复
while(middle < right && nums[middle] == nums[++middle]); // 并跳过重复
}
}
}
return res;
}
}F10 - 🟩1. 两数之和
解题
我先想到用 Arrays.sort() 解题,可发现结果要返回的是初始位置而不是位置上的数字。
如果用穷举,要用 O(N2) 复杂度寻找 target - x ,时间复杂度过高。
所以可以用 哈希表 解决寻找 target - x 时间复杂度过高的问题,时间复杂度从 O(N2) 降低到 O(N)
class Solution{
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target){
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(map.containsKey(target - nums[i])){
return new int[]{map.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
}
return new int[0];
}F11 - 🟨5. 最长回文子串
解题
- 方法1
- 暴力求解
- 时间复杂度 O(n^3), 左指针从0开始,右指针从L+1开始,对所有长度大于2的字符串进行 validPalindromic() 判断,找出 maxLen
- 方法2 +
F59 - 🟥239. 滑动窗口最大值
解题
单调队列
- 遍历给定数组中的元素,如果队列不为空且当前元素大于等于队尾元素,则将队尾元素移除。直到,队列为空或当前考察元素小于新的队尾元素;
- 当队首元素的下标小于滑动窗口左侧边界left时,表示队首元素已经不再滑动窗口内,因此将其从队首移除。
- 由于数组下标从0开始,因此当窗口左边界大于等于0时,意味着窗口形成。此时,队首元素就是该窗口内的最大值。
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int[] res = new int[nums.length - k + 1];
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for(int right = 0; right < nums.length; right++){
while(!queue.isEmpty() && nums[queue.peekLast()] < nums[right]){
queue.removeLast();
}
queue.addLast(right);
int left = right - k + 1;
if(queue.peekFirst() < left){
queue.removeFirst();
}
if(left >= 0){
res[left] = nums[queue.peekFirst()];
}
}
return res;
}
}F87 - 🟨695. 岛屿的最大面积
解题
深度优先搜索
- 我们想知道网格中每个连通形状的面积,然后取最大值。
- 如果我们在一个土地上,以 444 个方向探索与之相连的每一个土地(以及与这些土地相连的土地),那么探索过的土地总数将是该连通形状的面积。
- 为了确保每个土地访问不超过一次,我们每次经过一块土地时,将这块土地的值置为 000。这样我们就不会多次访问同一土地。
class Solution {
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[i].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
res = Math.max(res, dfs(i, j, grid));
}
}
}
return res;
}
// 每次调用的时候默认num为1,进入后判断如果不是岛屿,则直接返回0,就可以避免预防错误的情况。
// 每次找到岛屿,则直接把找到的岛屿改成0,这是传说中的沉岛思想,就是遇到岛屿就把他和周围的全部沉默。
// ps:如果能用沉岛思想,那么自然可以用朋友圈思想。有兴趣的朋友可以去尝试。
private int dfs(int i, int j, int[][] grid) {
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= grid.length || j >= grid[i].length || grid[i][j] == 0) {
return 0;
}
grid[i][j] = 0;
int num = 1;
num += dfs(i + 1, j, grid);
num += dfs(i - 1, j, grid);
num += dfs(i, j + 1, grid);
num += dfs(i, j - 1, grid);
return num;
}
}F105 - 🟨739. 每日温度
关键字
| 关键字 | 模式识别 |
|---|---|
| “下一个更大元素” “下一个更小元素” “连续子数组” “某种最值” | 单调栈(通常是递增或递减) |
解题
- 遍历每日温度,维护一个单调栈
- 若栈为空或者当日温度<=栈顶温度则直接入栈
- 反之 > 的话,说明栈顶元素的升温日找到,将栈顶元素出栈,计算两个日期相差的天数即可。
- 栈里存日期还是存温度:要求的是升温的天数,而不是温度。所以栈中存下标而非温度
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
int[] answer = new int[temperatures.length];
for(int i = 0; i < temperatures.length; i++){
while(!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]){
int preHotDay = stack.pop();
answer[preHotDay] = i - preHotDay;
}
stack.push(i);
}
return answer;
}
}F199 - 🟨279. 完全平方数
关键字
| 关键字 | 模式匹配 |
|---|---|
| 可以拆分成子问题解决 如 “从结果倒推” 的爬楼梯问题 | 动态规划 |
解题
class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
// n + 1长度,0不用,使得 temp[n] 和 n 对其。值均为0
int[] temp = new int[n + 1];
for(int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++){
temp[i] = i;
for(int j = 1;(i - j * j) >= 0 ; j++){
temp[i] = Math.min(temp[i], temp[i - j * j] + 1);
}
}
return temp[n];
}
}