Various data types in C
C/C++ provides various data types that can be used in your programs.In general, you’d commonly use: int for most variables and “countable” things (for loop counts, variables, events). char for characters and strings. float for general measurable things (seconds, distance, temperature). uint32 for bit manipulations, especially on 32-bit registers.
- int for most variables and “countable” things (for loop counts, variables, events)
- char for characters and strings
- float for general measurable things (seconds, distance, temperature)
- uint32_t for bit manipulations, especially on 32-bit registers
Integer Data Types
| C type | alias | Bits | Sign | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| char | int8 | 8 | Signed | -128 .. 127 |
| unsigned char | uint8 | 8 | Unsigned | 0 .. 255 |
| short | int16 | 16 | Signed | -32,768 .. 32,767 |
| unsigned short | uint16 | 16 | Unsigned | 0 .. 65,535 |
| int | int32 | 32 | Signed | -2,147,483,648 .. 2,147,483,647 |
| unsigned int | uint32 | 32 | Unsigned | 0 .. 4,294,967,295 |
| long long | int64 | 64 | Signed | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 .. 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
| unsigned long long | uint64 | 64 | Unsigned | 0 .. 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 |
Floating Point Data Types
| C type | IEE754 Name | Bits | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| float | Single Precision | 32 | -3.4E38 .. 3.4E38 |
| double | Double Precision | 64 | -1.7E308 .. 1.7E308 |
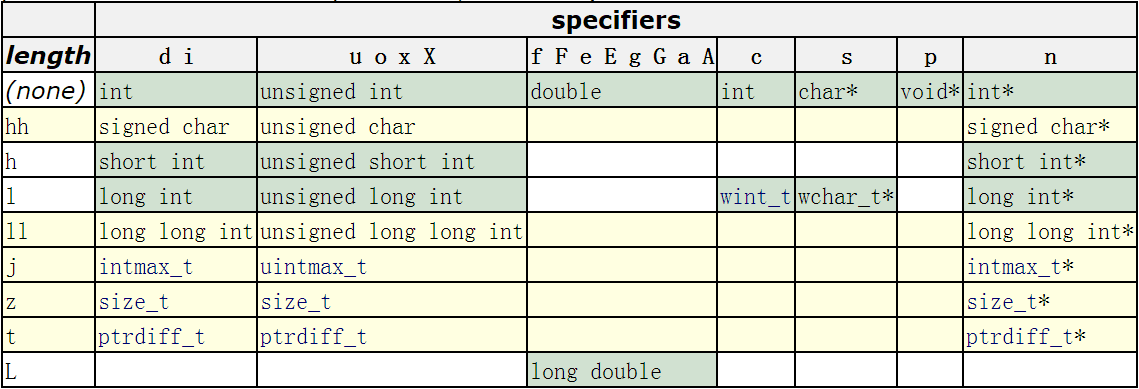
Print format
| |
1. Type
| 字符 | 对应数据类型 | 含义 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| d/i | int | 输出十进制有符号32bits整数,i是老式写法 | printf("%i",123);输出123 |
| o | unsigned int | 无符号8进制(octal)整数(不输出前缀0) | printf("0%o",123);输出0173 |
| u | unsigned int | 无符号10进制整数 | printf("%u",123);输出123 |
| x/X | unsigned int | 无符号16进制整数,x对应的是abcdef,X对应的是ABCDEF(不输出前缀0x) | printf("0x%x 0x%X",123,123);输出0x7b 0x7B |
| f/lf | float(double) | 单精度浮点数用f,双精度浮点数用lf(printf可混用,但scanf不能混用) | printf("%.9f %.9lf",0.000000123,0.000000123);输出0.000000123 0.000000123。注意指定精度,否则printf默认精确到小数点后六位 |
| F | float(double) | 与f格式相同,只不过 infinity 和 nan 输出为大写形式。 | 例如printf("%f %F %f %F\n",INFINITY,INFINITY,NAN,NAN);输出结果为inf INF nan NAN |
| e/E | float(double) | 科学计数法,使用指数(Exponent)表示浮点数,此处”e”的大小写代表在输出时“e”的大小写 | printf("%e %E",0.000000123,0.000000123);输出1.230000e-07 1.230000E-07 |
| g | float(double) | 根据数值的长度,选择以最短的方式输出,%f或%e | printf("%g %g",0.000000123,0.123);输出1.23e-07 0.123 |
| G | float(double) | 根据数值的长度,选择以最短的方式输出,%f或%E | printf("%G %G",0.000000123,0.123);输出1.23E-07 0.123 |
| c | char | 字符型。可以把输入的数字按照ASCII码相应转换为对应的字符 | printf("%c\n",64)输出A |
| s | char* | 字符串。输出字符串中的字符直至字符串中的空字符(字符串以空字符’\0‘结尾) | printf("%s","测试test");输出:测试test |
| S | wchar_t* | 宽字符串。输出字符串中的字符直至字符串中的空字符(宽字符串以两个空字符’\0‘结尾) | setlocale(LC_ALL,"zh_CN.UTF-8"); wchar_t wtest[]=L"测试Test"; printf("%S\n",wtest); 输出:测试test |
| p | void* | 以16进制形式输出指针 | printf("%010p","lvlv");输出:0x004007e6 |
| n | int* | 什么也不输出。%n对应的参数是一个指向signed int的指针,在此之前输出的字符数将存储到指针所指的位置 | int num=0; printf("lvlv%n",&num); printf("num:%d",num); 输出:lvlvnum:4 |
| m | 无 | 打印errno值对应的出错内容 | printf("%m\n"); |
| a/A | float(double) | 十六进制p计数法输出浮点数,a为小写,A为大写 | printf("%a %A",15.15,15.15);输出:0x1.e4ccccccccccdp+3 0X1.E4CCCCCCCCCCDP+3 |
2. Flags
| 字符 | 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| - | 减号 | 结果左对齐,右边填空格。默认是右对齐,左边填空格。 |
| + | 加号 | 输出符号(正号或负号) |
| space | 空格 | 输出值为正时加上空格,为负时加上负号 |
| # | 井号 | type是o、x、X时,增加前缀0、0x、0X。 type是a、A、e、E、f、g、G时,一定使用小数点。默认的,如果使用.0控制不输出小数部分,则不输出小数点。 type是g、G时,尾部的0保留。 |
| 0 | 数字零 | 将输出的前面补上0,直到占满指定列宽为止(不可以搭配使用“-”) |
example:
| |
3. width
输出最小宽度
| width | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 数值 | 十进制整数 | printf("%06d",1000);输出:001000 |
| * | 星号。不显示指明输出最小宽度,而是以星号代替,在printf的输出参数列表中给出 | printf("%0*d",6,1000);输出:001000 |
4. precision
| .precision | 描述 |
|---|---|
| .数值 | 十进制整数。 (1)对于整型(d,i,o,u,x,X),precision表示输出的最小的数字个数,不足补前导零,超过不截断。 (2)对于浮点型(a, A, e, E, f ),precision表示小数点后数值位数,默认为六位,不足补后置0,超过则截断。 (3)对于类型说明符g或G,表示可输出的最大有效数字。 (4)对于字符串(s),precision表示最大可输出字符数,不足正常输出,超过则截断。 precision不显示指定,则默认为0 |
| .* | 以星号代替数值,类似于width中的*,在输出参数列表中指定精度。 |
5. length
类型长度指明待输出数据的长度。因为相同类型可以有不同的长度,比如整型有16bits的short int,32bits的int,也有64bits的long int,浮点型有32bits的单精度float和64bits的双精度double。为了指明同一类型的不同长度,于是乎,类型长度(length)应运而生,成为格式控制字符串的一部分。